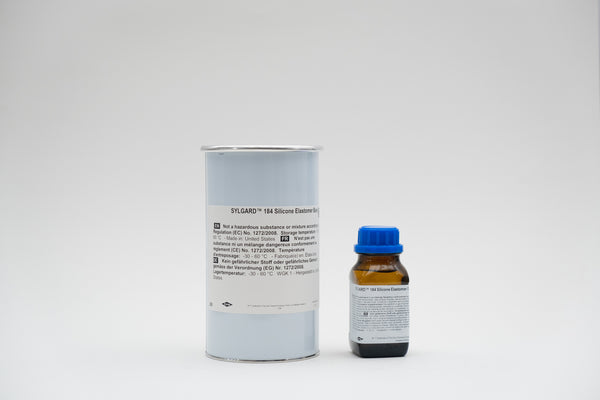
SYLGARD™ 184 Silicone Elastomer
Silicone elastomer hermetic
Transparent Hermetic silicone sealant for electronics with good fire resistance, Two-component set
Application:
- LED lighting encapsulation
- Power supplies
- Connectors
- Sensors
- Industrial control
- Transformers
- Amplifiers
- High Voltage Resistor Kits
- Relays
- Solar Cell Glue/Capsule
- glue of the guide wire to the integrated circuits during processing
- Silicone Compound for Electronics in Refrigeration
Features and benefits:
- Liquid
- Cure at room temperature or hot
- Good dielectric properties
- Fast, versatile, temperature-controlled curing processing
- High transparency allows easy inspection of components
- Flammability class UL 94 V-1
- UL 746C Recognition
Composition
- Two-piece
- Mixing ratio 10 to 1
- Polydimethylsiloxane elastomer
Description
Dow silicone encapsulation is supplied as two-part 10 to 1 liquid component kits. When the liquid components are thoroughly mixed, the mixture cures to a flexible elastomer that is ideal for protecting electrical/PCB assembly applications. Dow silicone encapsulations cure without exotherm at a constant rate, regardless of section thickness or degree of confinement.
Typical Properties
| Characteristic | Unit | Result |
| One or two parts | Two | |
| Color | Colorless | |
| Viscosity (base) | cP | 5100 |
| Hardness | medium stiffness | 20A-50A |
| PA | 5.1 | |
| Viscosity (mixed) | cP | 3500 |
| PA | 3.5 | |
| Thermal conductivity | btu/hr ft °F | 0.15 |
| W/m °K | 0.27 | |
| Specific gravity (hardened) | 1.03 | |
| Operating time at 25°C (lifetime - hours) | hours | 1.5 |
| Curing time at 25°C | hours | 48 |
| Curing time at 100°C | minutes | 35 |
| Curing time at 125°C | minutes | 20 |
| Curing time at 150°C | minutes | 10 |
| Edge of Hardness | 43 | |
| Dielectric strength | volts/miles | 500 |
| kV/mm | 19 | |
| Volume resistivity | ohm*cm | 2.9E+14 |
| Dissipation factor at 100 Hz | 0.00257 | |
| Dissipation factor at 100kHz | 0.00133 | |
| Dielectric constant at 100 Hz | 2.72 | |
| Dielectric constant at 100 kHz | 2.68 | |
| Linear CTE (by DMA) | ppm/°C | 340 |
| Tensile strength | PSI | 980 |
| MPa | 6.7 | |
| kg/cm2 | 69 | |
| Refractive index | @ 589nm | 1.4118 |
| Refractive index | @ 632.8nm | 1.4225 |
| Refractive index | @1321nm | 1.4028 |
| Refractive index | @ 1554nm | 1.3997 |
| UL RTI Rating | °C | 150 |
Certificates and standards
- MIL specification,
- UL recognition
How to use
Application Methods
• Automatic mixing and dosing
• Hand mixing
Mixing and venting
The 10 to 1 mix ratio in which these products are supplied gives one the freedom to adjust the modulus and hardness to the specific needs of the application and production lines. In most cases, venting is not required.
Preparation of the substrate
Many silicone casings will require a primer for adhesion applications. For best results, the primer should be applied in a very thin, uniform layer and then wiped off after application. Once applied, it should be thoroughly cured before the silicone elastomer is applied.
Processing / Curing
The thoroughly mixed Dow silicone capsule can be poured/dispensed directly into the container in which it is to be cured. Whenever possible, pouring/dispensing should be done under vacuum, especially if the component being poured or encapsulated has many small voids. If this technique cannot be used, the equipment should be evacuated after pouring/dispensing the silicone capsule. Dow silicone casings can be cured at room temperature (25°C/77°F) or by heat. Room temperature curing encapsulants can also be accelerated by heat for faster cure.
Durability and curing speed
The curing reaction begins with the mixing process. Initially, curing is indicated by a gradual increase in viscosity, followed by gelation and conversion to a solid elastomer. Pot life is defined as the time required for the viscosity to double after mixing the base and curing agent and is highly dependent on temperature and application. Please refer to the data table.
Useful temperature ranges
In most applications, silicone elastomers should operate in a temperature range of -45 to 200°C (-49 to 392°F) for extended periods. However, at the extreme ends of the spectrum, they should be adequately tested for the specific end-use environment. For low-temperature performance, thermal cycling to conditions such as -55°C (-67°F) may be possible, but the performance of the part or assembly should be verified.
Compatibility
Certain materials, chemicals, hardeners and plasticizers may inhibit the cure of addition-cured gels. The most important of these are: organotin and other organometallic compounds, silicone rubber containing an organotin catalyst, sulfur, polysulfides, polysulfones or other sulfur-containing materials, unsaturated hydrocarbon plasticizers and some solder flux residues. If the substrate or material is in question with respect to potential cure inhibition, it is recommended that a small-scale compatibility test be conducted to determine suitability for the application. The presence of liquid or uncured product at the interface between the questionable substrate and the cured gel indicates incompatibility.
Repair and removal
In the manufacturing of electrical devices and PCB assemblies, it is often desirable to recover or reclaim damaged or defective units.
Dow silicone capsules can be selectively removed with relative ease. To remove silicone elastomers, simply cut with a sharp blade or knife to break and remove unwanted material from the area to be repaired. Sections of bonded elastomer are best removed from substrates and circuits by mechanical means such as scraping or rubbing, and can be aided by using DOWSIL™ OS Fluids to swell the elastomer.
Product title
Vendor
19,99 zl PLN | 24,99 zl PLN
Product title
Vendor
19,99 zl PLN | 24,99 zl PLN
Product title
Vendor
19,99 zl PLN | 24,99 zl PLN
Product title
Vendor